
Influence of the Arabic Language
As one of the oldest and commonly wide spoken language, it’s not surprising that the Arabic language has influenced many other languages in the world.
In Europe, both Latin and Greek have been influenced by the Arabic Language. Hence, much of the Romance languages such as Portuguese, Spanish, Catalan and Sicilian borrow many vocabulary words from Arabic.
Its influence can be seen in Turkish, Kurdish, Persian and Urdu. The African languages of Somali and Swahili have also been touched by the Arabic Languages. The influence of the language has also reached the languages spoken in Asia, such as Hindi, Malay, Indonesian, Pashto, Punjabi, Sindhi, Hausa, and Tagalog. At the same time, many English words borrowed heavily from the Arabic language.
Arabic Calligraph is a Visual Art
Arabic letters are always joined together in words, even when typed, leaving the impression that all scripts are handwritten.
There are no handwritten and typed letters, no capital letters either. It is different than the other languages. There’s only one set of symbols that goes for all occasions.
Each letter takes different forms depending on its place inside the word – at the beginning, in the middle, at the end, or isolated.
Scribes and calligraphers have developed various types of script over the years.
Now it is being celebrated in all its forms, with Saudi Arabia extending the year of Arabic Calligraphy into 2021 and UNESCO registering the art form on its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Arabic calligraphy is taking its rightful place at the heart of Arab identity.
As the Iraqi calligrapher Wissam Shawkat says:
“This is the one thing that is pure for us” (Arab News- Introduction)


According to various sources, the first manifestations of the language appear to go back to the second millennium BC. Arabic belongs to the Semitic family of languages, which also includes Hebrew, Aramaic, and -Phoenician.
Arabic is descended from a language known in the literature as Proto-Semitic. This relationship places Arabic firmly in the Afro-Asiatic group of world languages. Going further into the relationship between Arabic and the other Semitic languages, Modern Arabic is part of the central group of the Western Semitic languages.
Arabic is a very rich language, which is full of vocabulary. As an example, the Arabic names of day timing are amazing! each hour in the day has a name
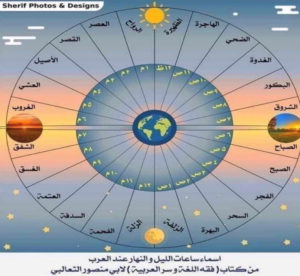
And more than 100 names for camels. The linguistic lexicon capacity of the Arabic Language is 12 million words, out of which only 400,000 are used.
It has different dialects and different calligraphic forms and styles.
Arab colloquial dialects are generally only spoken languages. Arabs use the colloquial language in all their daily interactions, but, when they encounter a language situation calling for greater formality, Modern Standard Arabic is the center of choice.
Modern Standard Arabic is used in reading, writing, and high register speech. It is descended from the Classical language of the Qur’an and, in the view of almost all Arabs, is the “pure” Arabic. However, Modern Standard Arabic is a learned language, and it is one of the six most spoken languages in the world, comprising more than 400 million speakers.
This form of Arabic goes back to pre-Islamic poetry and is an elegant, or clear form of Arabic. Muslim scholars say that initially the Quran was revealed by Allah Almighty and taught by the ¬Prophet ¬Mohammed in seven types of ¬Qera’at (readings). At the time, they were the most dominant dialects in spoken Arabic. The Qur’an has served as the basis of the Arabic language to this day.


